Importing data into Firestore using Python Part 1

I’m a big fan of Firebase and have been using it to develop projects for a while, however I was struggling to find a simple way to import a large quantity of data into Firestore. The Realtime database has a nice import and export data functionality but currently no equivalent exists for Firestore, so I thought I’d use a Python script to achieve this.
Before we start, I’m assuming you have a project already setup in Firebase and are using Firestore, if not you can find the guides for how to here.
Generating Service Account Key
To use the SDK we’ll need to have a Service Account Key. You can generate this by using Firebase Console > Project Settings:
Then selecting Service accounts and clicking Generate new private key
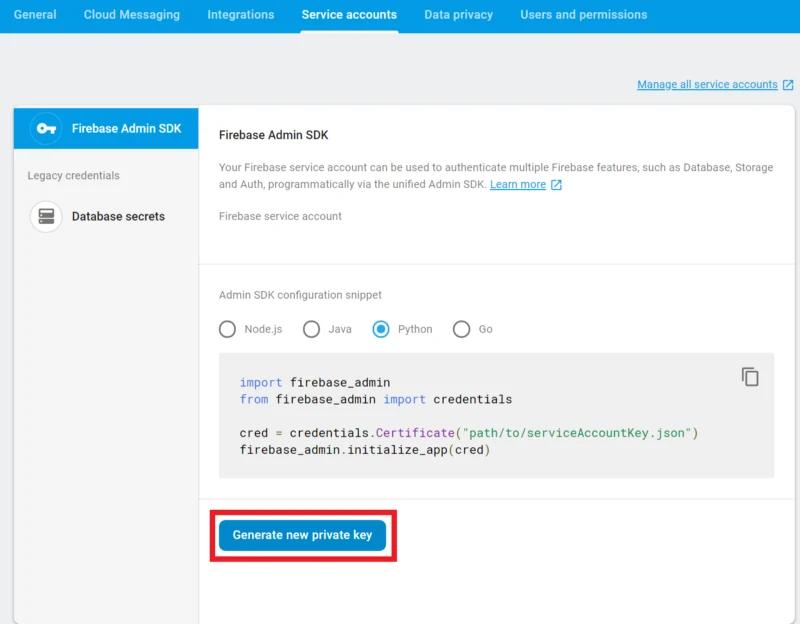
This will produce a .json file with the credentials needed to access the Firebase project.
IMPORTANT! Keep this confidential, don’t add it to version control or to a client side application.
Setting up Python project
Now that we have got the Service Account Key we can set up the Python project, if you are used to setting up python projects obviously do this in your preferred way, but just in case.
Assuming you’ve got a version of Python installed, I would recommend at least 3.4 and also using a virtualenv Create a folder for the project and initialise the virtual environment using:
virtualenv envOnce completed type the path to the activate script in the virtual environment this is located in env\scripts folder forexample: .\env\Scripts\activate.bat
This starts the environment for use in the terminal you’ll see it’s name in front of the prompt i.e. (env)
Then install:
pip install firebase-admin google-cloud-firestoreThis provides firebase-admin package to allow the connections as well as the google-cloud-firestore package.
Move your copy of the Service Account Key to the working folder, and for ease I renamed mine to ServiceAccountKey.json. It’s probably a good time to add it to your .gitignore file, if using git, to avoid accidentally committing it.
Connecting to Firestore
You can now connect to the Firestore for your project, I’ll just demonstrate how to do this and get some data then go on to adding data imported from a csv file.
Add a main.py file to the folder with the below:
import firebase_admin
import google.cloud
from firebase_admin import credentials, firestore
cred = credentials.Certificate("./ServiceAccountKey.json")
app = firebase_admin.initialize_app(cred)
store = firestore.client()
doc_ref = store.collection(u'users').limit(2)
try:
docs = doc_ref.get()
for doc in docs:
print(u'Doc Data:{}'.format(doc.to_dict()))
except google.cloud.exceptions.NotFound:
print(u'Missing data')This reads from the collection users, limiting the returned results to just 2 as I didn’t want all of the users collection returned. The script then prints the data as a dictionary.
Now we can connect and get data, lets add some to Firestore, just by changing the main.py to below, we can add a collection called test and a new document with the attributes of name and added and their values.
import firebase_admin
import google.cloud
from firebase_admin import credentials, firestore
cred = credentials.Certificate("./ServiceAccountKey.json")
app = firebase_admin.initialize_app(cred)
store = firestore.client()
doc_ref = store.collection(u'test')
doc_ref.add({u'name': u'test', u'added': u'just now'})Adding Data from csv to Firestore
Adding data from a csv file requires us to read the csv in and then group the data to be added into transactions of up to 500 as the Firestore batch writes function has a limit of this.
For this example I’m just using a flat data structure but you could expand upon this to allow for more complex structures to be added.
I’ve got a list of UK based breweries and want to add this to a new Firestore collection.
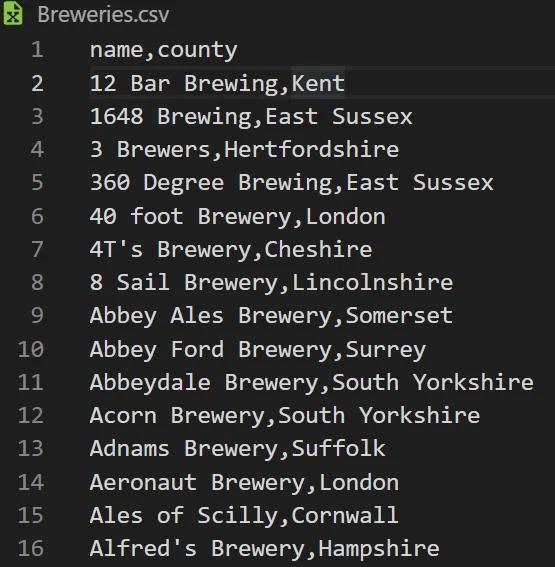
The file contains Name and County fields for each brewery and I’ve cleaned the data beforehand, so there are no empty values.
We can now update the main.py file to below, changing the CSV_FILE_PATH and COLLECTION_TO_ADD_TO variables to appropriate values, in my case Breweries.csv and breweries respectively.
import csv
import firebase_admin
import google.cloud
from firebase_admin import credentials, firestore
cred = credentials.Certificate("./ServiceAccountKey.json")
app = firebase_admin.initialize_app(cred)
store = firestore.client()
file_path = "CSV_FILE_PATH"
collection_name = "COLLECTION_TO_ADD_TO"
def batch_data(iterable, n=1):
l = len(iterable)
for ndx in range(0, l, n):
yield iterable[ndx:min(ndx + n, l)]
data = []
headers = []
with open(file_path) as csv_file:
csv_reader = csv.reader(csv_file, delimiter=',')
line_count = 0
for row in csv_reader:
if line_count == 0:
for header in row:
headers.append(header)
line_count += 1
else:
obj = {}
for idx, item in enumerate(row):
obj[headers[idx]] = item
data.append(obj)
line_count += 1
print(f'Processed {line_count} lines.')
for batched_data in batch_data(data, 499):
batch = store.batch()
for data_item in batched_data:
doc_ref = store.collection(collection_name).document()
batch.set(doc_ref, data_item)
batch.commit()
print('Done')Note: This script makes some assumptions to be aware of, the csv file’s first row are headers which are used to be the property names of the following rows i.e.
name,county
item1,item2
becomes { name: item1, county: item2}
We’ve also used the batch function from the Firestore client, this allows for set(), update() and delete() operations. Therefore to add a new document we must first create a new document (line 42) and then set the data for it in the batch (line 43).
The function batch_data is to restrict the operations per batch to the Firestore limit of 500, I used 499 to be safe.
Running the script now populates the Firestore collection with the values in the csv.
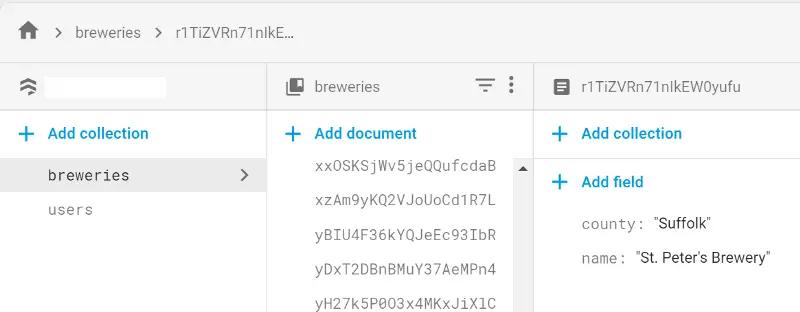
You can also retrieve the data from and compare it with the original data to check the process using a script similar to:
import firebase_admin
from firebase_admin import credentials, firestore
cred = credentials.Certificate("./ServiceAccountKey.json")
app = firebase_admin.initialize_app(cred)
store = firestore.client()
doc_ref = store.collection(u'COLLECTION_TO_CHECK')
data = []
docs = doc_ref.get()
for doc in docs:
data.append(doc.to_dict())
print(len(data))This script gets a count of the data rows, by changing the COLLECTION_TO_CHECK variable to the collection you want to check.
Conclusion
This is a simple guide to using the Firestore Admin SDK with Python to add and retrieve data, you can adapt these scripts to do more complex actions. You could also change the data format being added to one with sub collections or different variable types.
Hopefully this has been helpful, thanks for reading.
A big thank you to @ThatJenPerson and the excellent video guide which was a huge help.
Orginially published on medium
- Firebase
- Firestore
- Python